Understanding when and how to remove honey bee hives is crucial for maintaining safety while preserving these vital pollinators. This guide will explore the life cycle, behavior, and habitats of honey bees, reasons for hive removal, and best practices for safely managing and relocating hives.
Understanding Honey Bees and Their Behavior
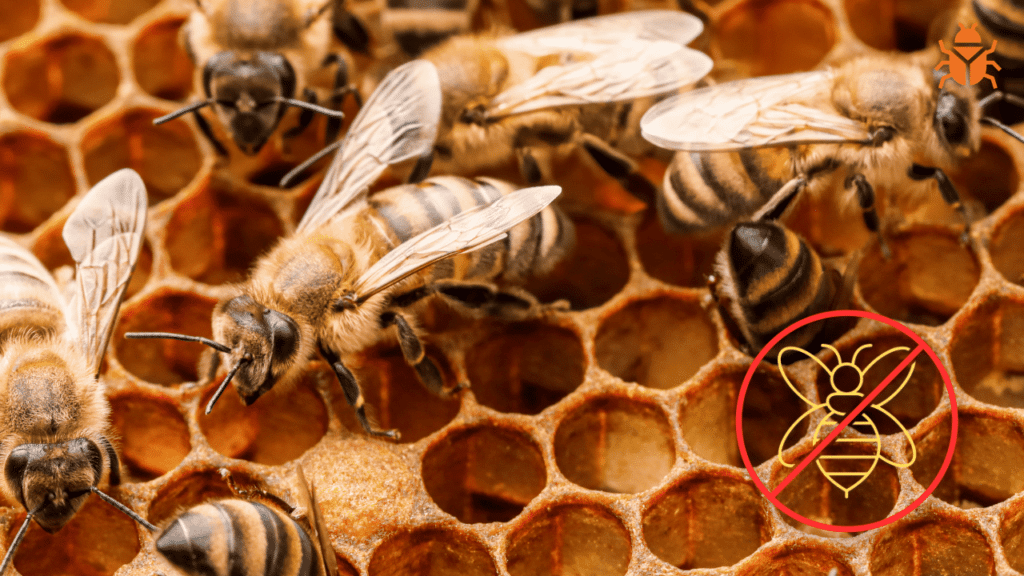
Life Cycle of Honey Bees
The life cycle of honey bees includes four main stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Knowledge of these stages is essential for recognizing bee activity and managing beehives appropriately.
Habitats and Beehives
Honey bees often build their hives in sheltered locations such as hollow trees, rock cavities, and occasionally within the structures of buildings. Early detection of these habitats can prevent large-scale infestations.
Behavioural Traits
Honey bees are generally non-aggressive and only sting when threatened. Understanding their behavior is crucial in determining the necessity and timing for hive removal.
Reasons for Beehive Removal
Safety Concerns
Beehives near human activity can pose safety risks, especially for individuals allergic to bee stings. Removing hives can reduce these health hazards.
Structural Risks
Beehives can cause structural damage over time as bees may burrow into wood or other materials, compromising building integrity.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
It’s important to consider local wildlife protection laws that may regulate the removal and relocation of beehives to protect bee populations.
DIY Beehive Removal: Steps and Safety Tips
Preparation
Suitable protective clothing should be worn during hive removal to prevent stings, including gloves, a veil, and a beekeeper suit.
Step-by-Step Guide
-
- Evaluate the Hive: Determine the size and accessibility.
-
- Time of Removal: Perform removal during early morning or late evening when bees are less active.
-
- Use of Smoke: Smoke helps to calm bees, making them less likely to sting during the process.
-
- Careful Removal: Gently remove the hive components and bees, aiming to keep the structure intact for relocation.
Post-Removal
Cleaning the area and sealing entry points are essential to prevent other bees from establishing a new colony in the same location.
Professional Beehive Removal Services
When to Call a Professional
For large or hard-to-reach hives, or when safety concerns are significant, professional removal services are recommended.
Choosing the Right Service
Select services that use humane methods for bee removal and relocation, ensuring the safety of both the bees and the people involved.
What to Expect
Professional services typically offer a comprehensive approach, from initial assessment to final cleanup, ensuring that bees are safely relocated and the area is secured against future infestations.
Preventive Measures and Bee Conservation
Preventing Reinfestation
Regular inspections and maintenance, such as sealing cracks and removing potential nesting sites, can prevent bees from returning.
Conservation Efforts
Supporting bee conservation can involve participating in or donating to local and national initiatives aimed at protecting pollinators.
Alternative Solutions
Non-lethal methods, such as relocating hives to areas where bees can thrive without human interference, are preferred to extermination.
Conclusion
Effective honey bee control and beehive removal require a balance between ensuring human safety and preserving the ecological benefits bees provide. Whether choosing DIY methods or professional services, understanding bee behavior and the appropriate removal techniques is essential for success.